What are exosomes?
Exosomes are small vesicles secreted by cells, with particle sizes between 30-150nm, almost all cells release exosomes into various body fluids, and they carry effective information about many host cells such as proteins, mRNA, miRNAs, and lipids.
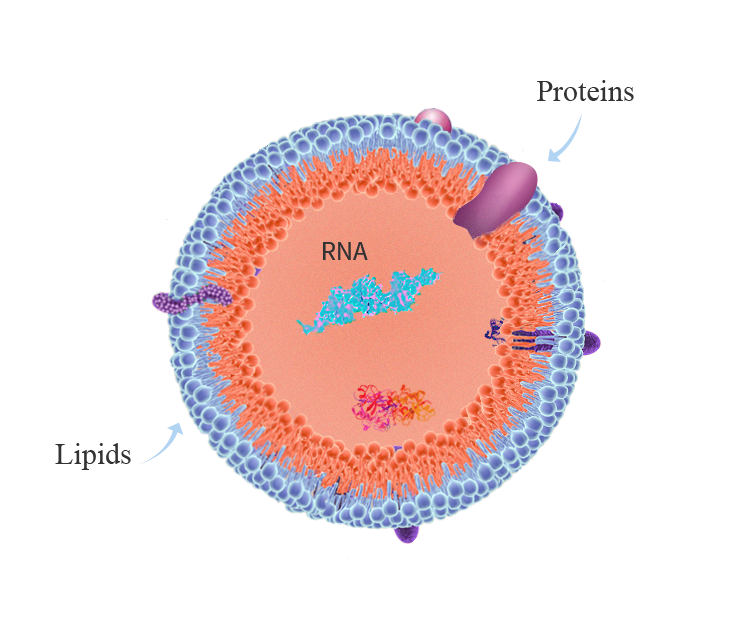
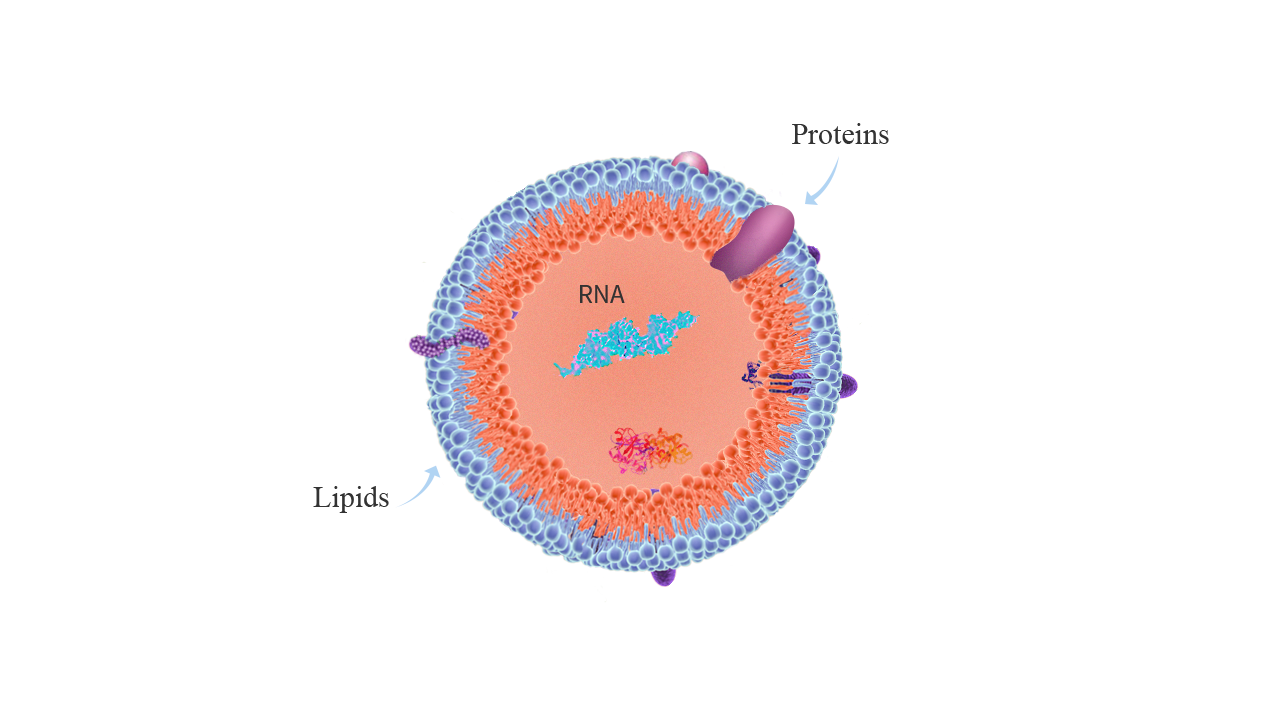
Intercellular messengers
As an important intercellular signal transduction molecule, exosomes can change the behavior of recipient cells and complete cell-to-cell signaling by transmitting information to recipient cells or activating their signaling pathways.
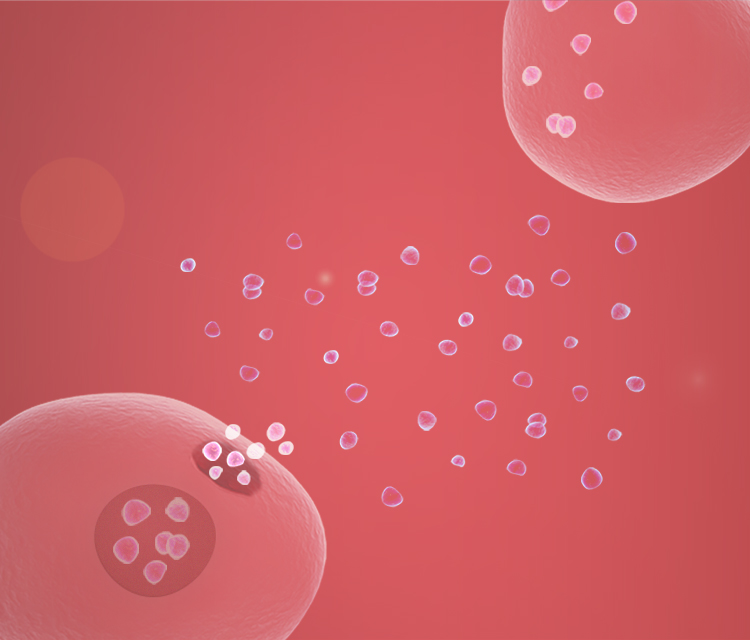
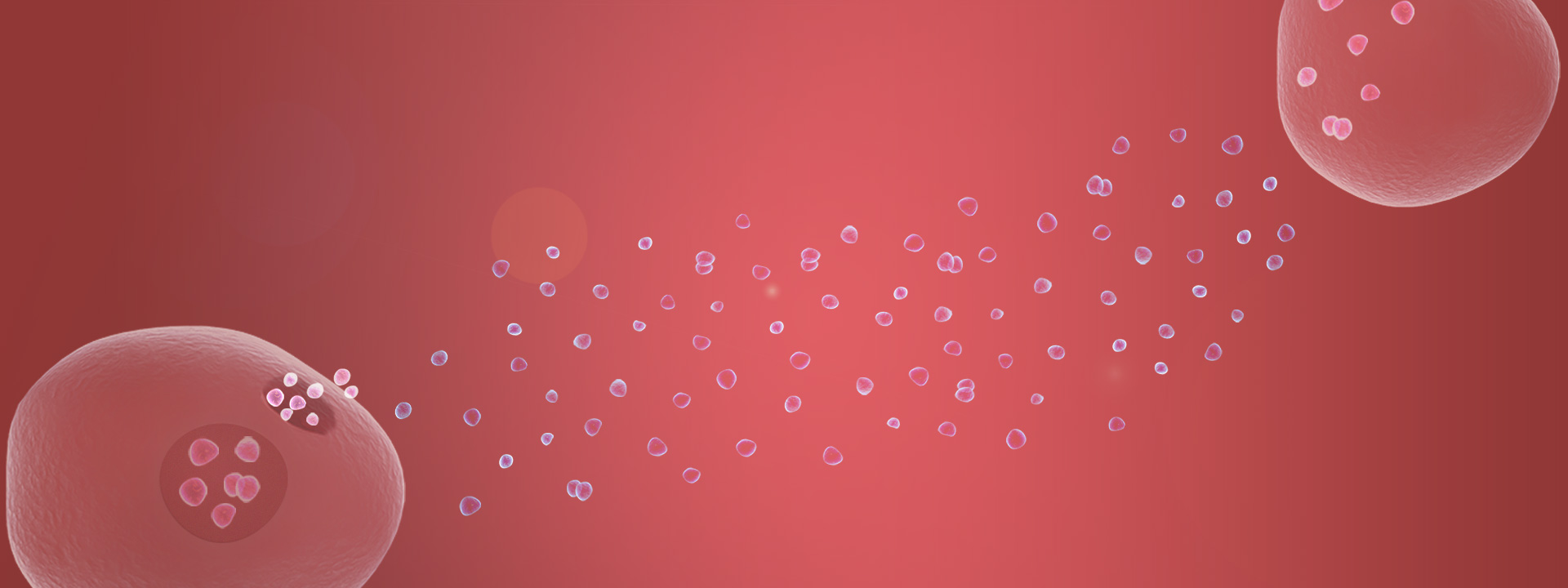
High heterogeneity
Different exosomes are released from different organs, tissues, cells, and even the same cell. High-precision and high-resolution exosome analysis can accurately reflect the state and biological significance of exosomes.

- Exosomes